
We canĭraw the Lewis structure on a sheet of paper. Lets consider the Lewis structure for CCl 4. Geometry is tetrahedral the bond angle is around 105 degrees. For bent molecular geometry when the electron-pair The bond angle is slightly less than 109.5 degrees, around 107ĭegrees. Geometry is trigonal planar the bond angle is slightly less thanġ20 degrees, around 118 degrees. Note: for bent molecular geometry when the electron-pair The table below summarizes the molecular and electron-pair geometriesįor different combinations of bonding groups and nonbonding pairs of electrons The Lewis structure and determine the number of bonding groups of electronsĪnd the number of non-bonding pairs of electrons on the central atom, then use That to determine the shape (molecular geometry) of a molecule you must write Notice that there are several examples with the sameĮlectron-pair geometry, but different molecular geometries. If askedįor the electron-pair geometry on the central atom we must respond with theĮlectron-pair geometry. The shape of a molecule we must respond with a molecular geometry. The molecular geometry is the shape of the molecule. To the bond angles of between a terminal-central-terminal atom in a compound. The electron-pair geometry provides a guide Molecular geometry is the name of the geometry used Name of the geometry of the electron-pair/groups/domains on the central atom, whether theyĪre bonding or non-bonding. In this case thereĪre three groups of electrons around the central atom and the molecualr geometry When a central atom has two terminal atoms bonded by single bonds and a terminalĪtom bonded with two pairs of electrons (a double bond). The term bonding groups/domains (second from the left column) is used in the columnįor the bonding pair of electrons.

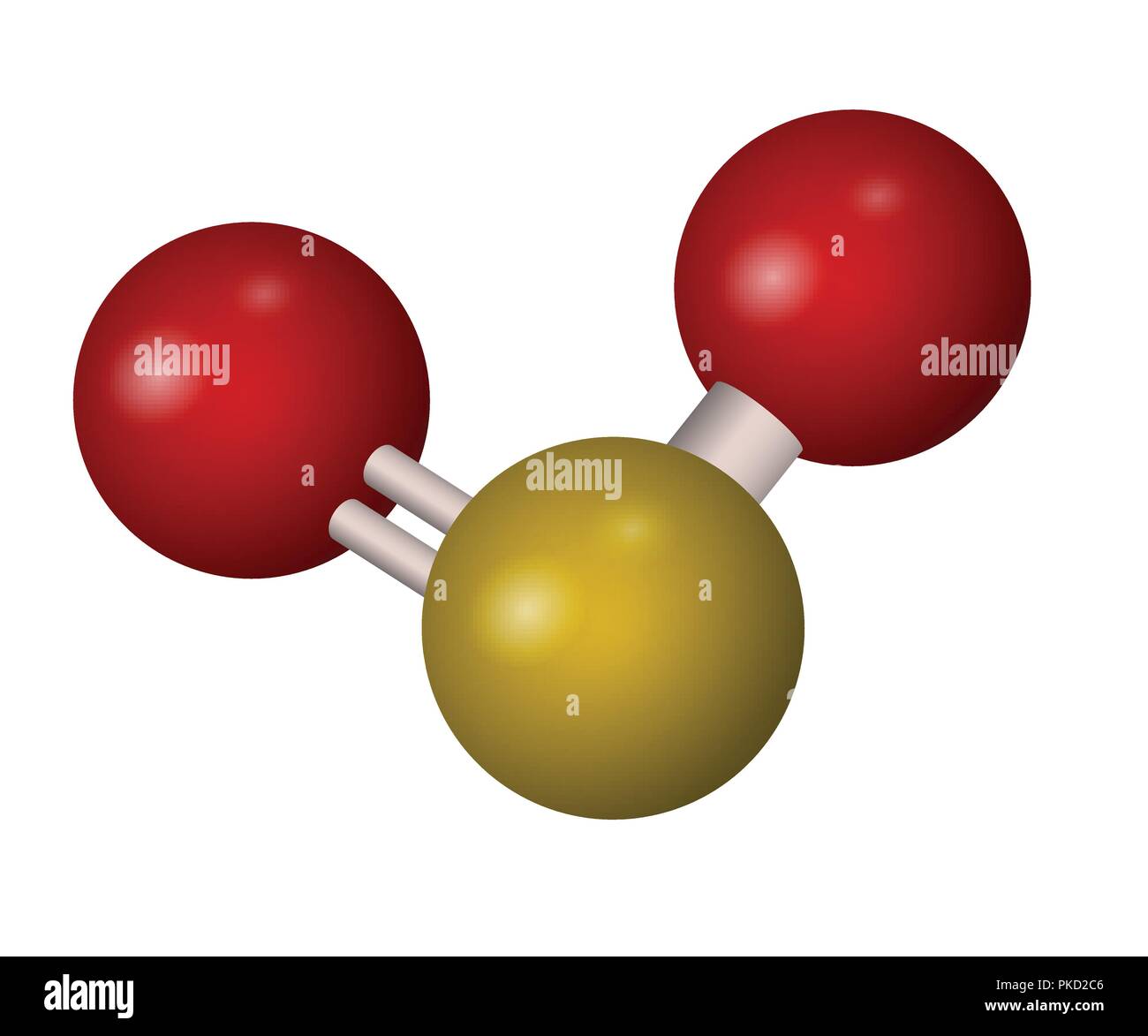
On an individual atom that are not shared with another atom. Non-bonding pairs of electrons are those pairs of electrons Of electrons are those electrons shared by the central atom and any atom to Of bonding pair of electrons and non-bonding pairs of electrons. The table below contains several columns. To use the model we will have to memorize a collection Model called the Valence Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) model that isīased on the repulsive behavior of electron-pairs. Of simple molecular (covalent) compounds and polyatomic ions. #O=S^(+)-O^-# is the standard representation proposed in texts and in schools ot chemistry.Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry VSEPR At this point we are ready to explore the three dimensional structure Note that the alternative Lewis structure #O=S=O# is still bent (why?), and entirely consistent with the structural parameters I have advanced.

The longer #S-O# bonds, and the more diffuse sulfur lone pair, tend to diminish the repulsive properties of the the sulfur lone pair. The actual which is only slightly compressed from the idealized trigonal planar geometry. Of course, the 2 oxygen atoms are entirely equivalent, and the resonance isomerism available to #O=S^(+)-O^-# does reflect this. Since for a Group 16 atom, there should be 6 valence electrons for neutrality, the assigned electronic charges are consistent with the Lewis representation. There are 18 electrons to distribute in the molecule, where sulfur, as the LEAST electronegative atom, will be central.Ī Lewis structure of #O=S^(+)-O^-# is reasonable, where from left to right as we face it, there are 6, 5, and 7 valence electrons. #"VSEPR"# predicts that sulfur dioxide should be a bent molecule, where, to a first approximation, Why?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
